This document was written for
BSD Today
and was
published on Feb 13th 2001.
Network Flight Instructions
Part II: Internet gateway configuration & basic online security rules
Hubert Feyrer, January 2001
Introduction
The first part of this article has given an overview of DSL, how it
works with NetBSD and how you can set it up. Now after you have
installed setup your shiny new DSL connection, some considerations
should be made about being online and utilizing the connection
while preparing for the less friendly side of "The Net". This part
of the article gives an overview of ways to use your DSL machine as
gateway for your home or office network, and goes through the basic
steps to setup and maintain security to machines connected directly
to the Internet.
Using your Internet access from more than one machine
* Masquerading many machines behind a single gateway
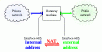
If you have several machines in your home or office network, make
the other machines use it. With NAT (or "IP masquerading", as
it's called in another universe), multiple machine can be hidden
behind one gateway machine. The machines behind the gateway can
use their own, private network numbers (usually form the 10/24 or
192.168/16 subnets), and the gateway will translate the private,
internal adresses to the public, external address of the gateway
machine (hence NAT => Network Address Translation, see Image
#3). Any replies made to requests sent out will be translated
before sent back to the client. One of the characteristics of
this scheme is that a client machine needs to establish a
connection, and no outside machine can connect beyond the NAT
gateway. From the security point of view this is absolutely
desirable. From a practical view, it might be needed to forward
single ports to inside machines, e.g. to let them handle WWW or
FTP requests.
|
Image #3: (click to enlarge!)
|
Please check the following links for further details. Providing
an in-depth description of of NAT is beyond the scope of this
article:
* Setup proxies for services: www (squid), ftp, ...
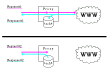
Setting up NAT allows several computers to share one network
connection, multiplexed via a NATing gateway. One other thing you
will want to setup after NAT is a caching proxy, to only fetch
any web pages (and images, etc.) if they haven't been fetched by
someone from your internal network recently. In that case the
proxy will safe the data to disk, and return that saved data
later when the same file is requested again, see Image #4. This
scheme is most efficient with static web pages and images, and it
can lead to a dramatic decrease of network ressource usage.
|
Image #4: (click to enlarge!)
|
Basic Online Security
(c) Copyright 2001 Hubert Feyrer
$Id: NFI-2.html,v 1.1 2001/02/01 04:03:46 feyrer Exp $

